Workbench Carpentries Repository Maintenance via Visual Studio Code
Is Visual Studio Code your home away from home? Have you been putting off getting up to speed on Carpentries Workbench due to lack of familiarity with R Studio? I have good news. With a little configuration you can maintain your Workbench based lessons from inside Visual Studio Code (VS Code) without the added cognitive load of a new IDE.
Installing R & Pandoc
You will still need to install R and Pandoc. While you technically won’t need R Studio, that is the most straighforward way to get both R and Pandoc installed, so I recommend doing it that way if you have not already. Get R Studio.
Add R extension to VS Code
Inside VS code, you will need the R extension. After the R extension is installed, VS code will prompt you to install the R Language Server and additional dependencies like rlang and jsonlite needed for VS Code to interact with the R interpreter installed on your system. Depending on where your R interpreter is installed and the file permissions, you may need to do this as an adminstrator. On my Windows machine, I had to run VS Code as an administrator just for the R Language Server to install. Once installed, it works fine as a regular user. If for some reason it fails to automatically prompt installation, you can try doing so from the R terminal. See R in Visual Studio Code for more guidance on that.
Install R Extension Figure
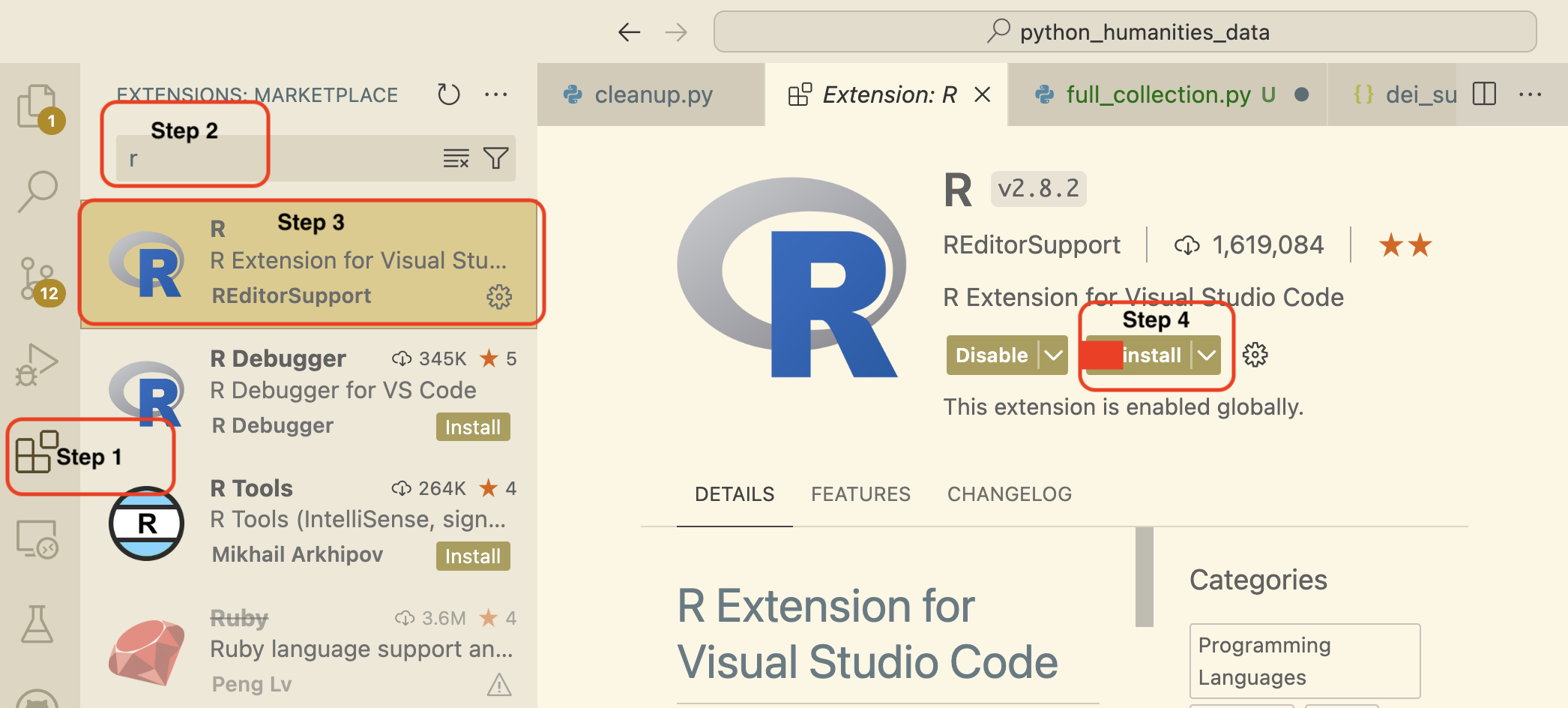
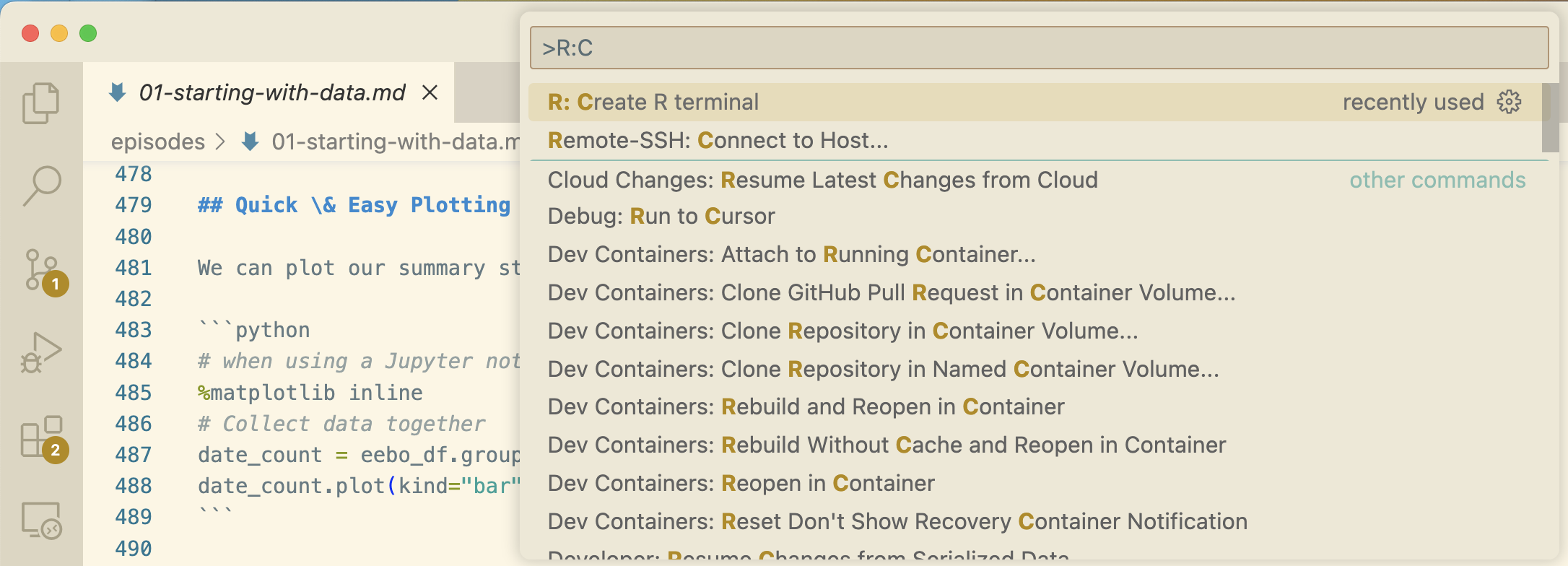
Once VS Code is configured to use R, open your Workbench based repository. Use Command-Shift-P on Mac or Ctrl-Shift-P on Windows to activate the command palette. From there, start typing “R: Create R Terminal” to find the command and launch an R terminal.
Create R Terminal Figure
Opened R Terminal Figure
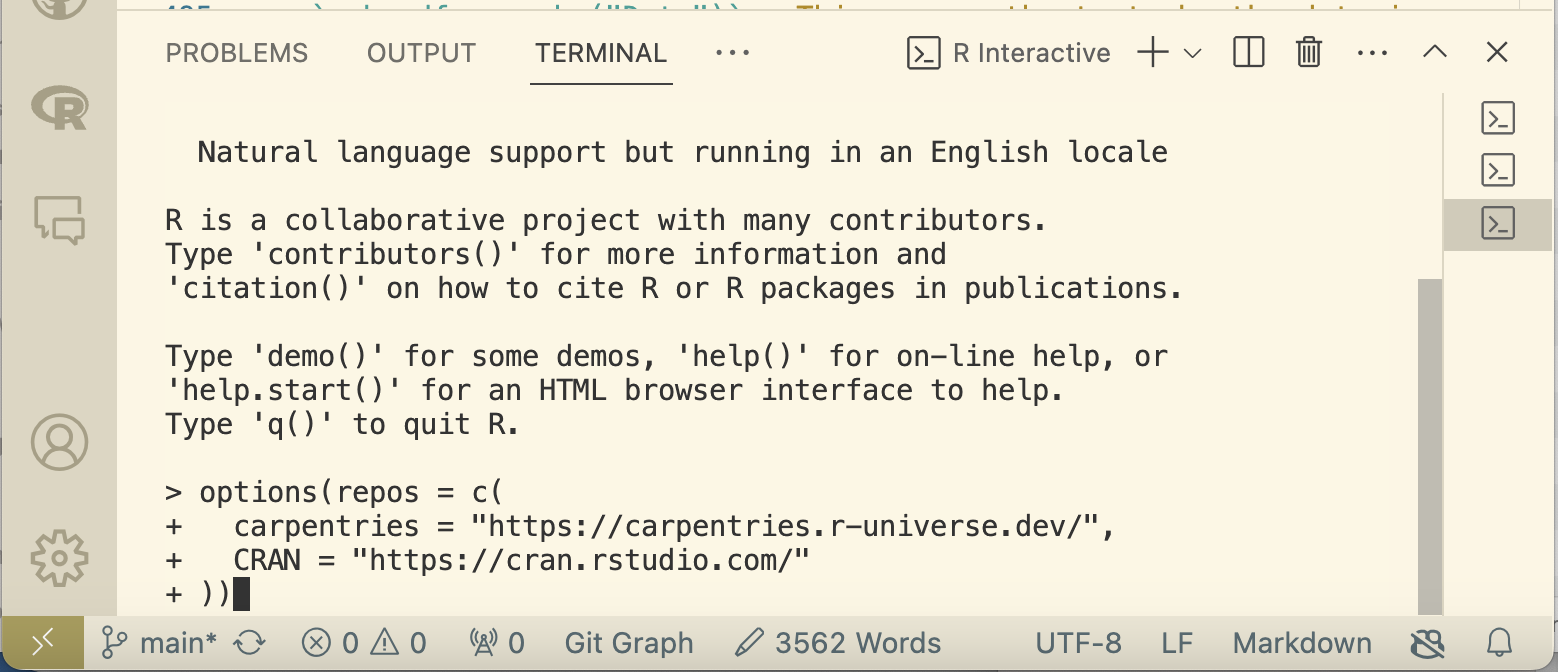
If you dont already have Carpentries Workbench previously installed, you will need to do so now by running these commands in your R terminal.
# register the repositories for The Carpentries and CRAN
options(repos = c(
carpentries = "https://carpentries.r-universe.dev/",
CRAN = "https://cran.rstudio.com/"
))
# Install the template packages to your R library
install.packages(c("sandpaper", "varnish", "pegboard", "tinkr"))
If you already had it installed, the install command above is also used to update, so you should probably go ahead and run that second command now for good measure.
Register R Repositories Figure
Install Workbench Figure
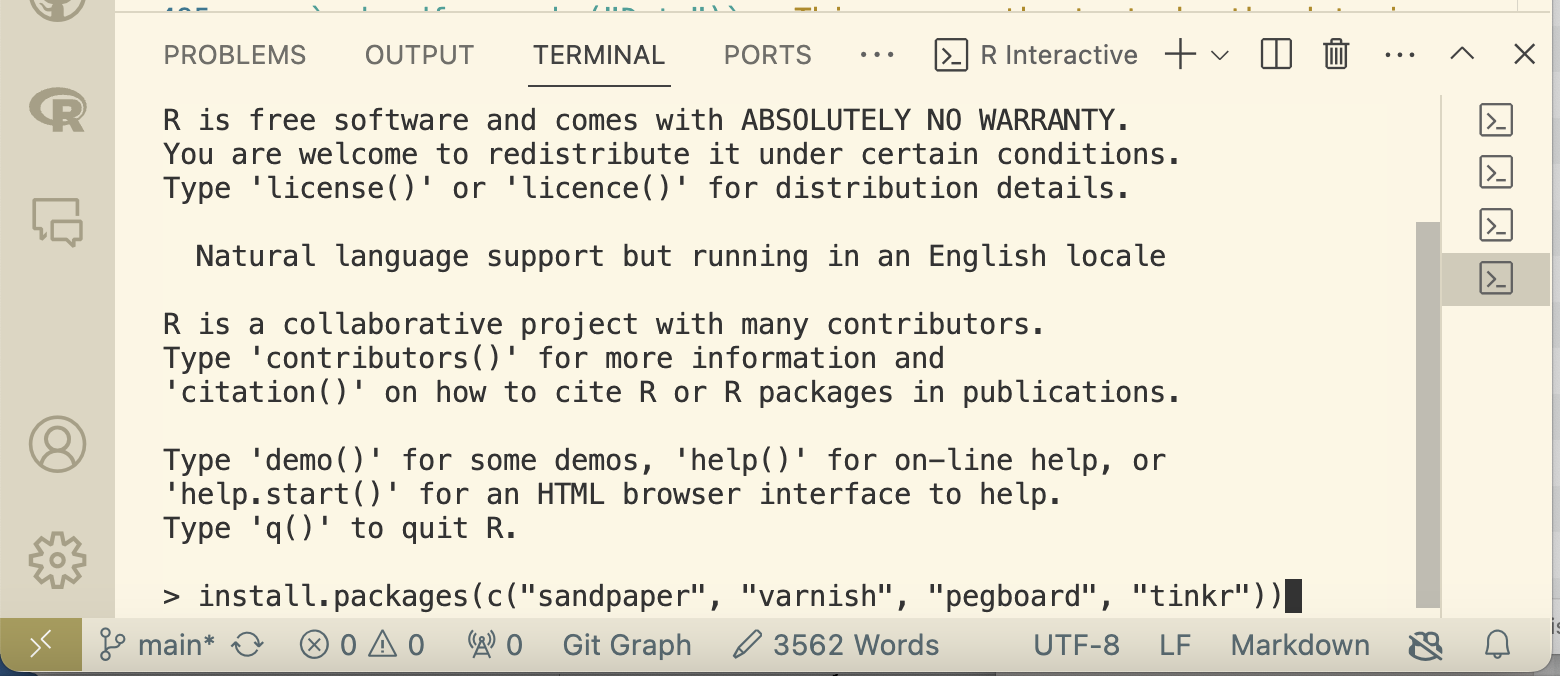
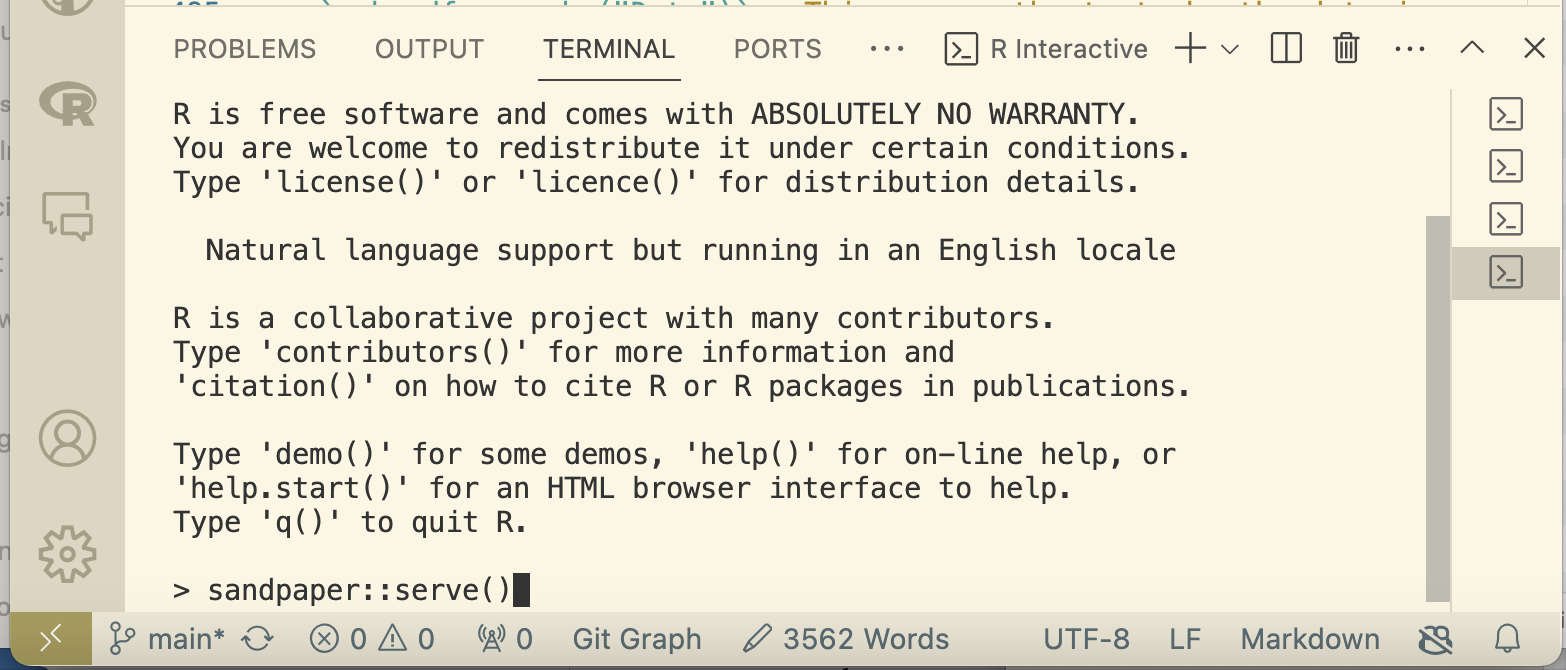
With Workbench installed, you can build and preview your Workbench based sites locally using sandpaper::serve() in the R terminal. It will appear in little window in the corner of the VS Code IDE by default, but you can use the link or url information in the R terminal to launch it in your default web browser. If you don’t already have a cloned repository to run this command on, you can use sandpaper::create_lesson("./your_lesson_name") in the R terminal to create one for testing.
sandpaper::serve() command figure
Web Preview Figure
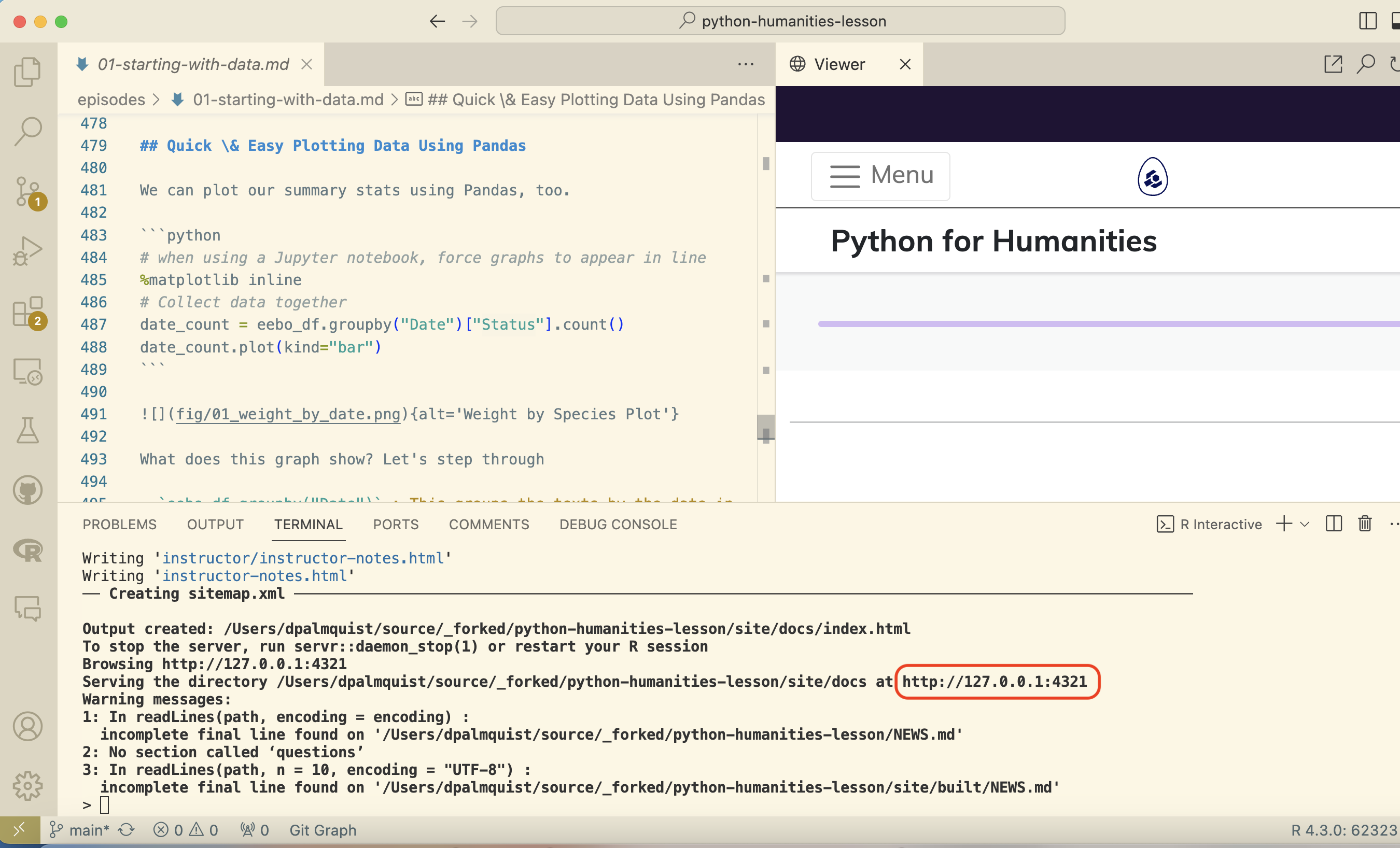
Commence editing your markdown files and the local preview site will rebuild each time you save. If you have read this far, I hope this guide has been of service to you. Happy Maintaining.
Dialogue & Discussion
Comments must follow our Code of Conduct.
